The needs and wants of consumers are constantly changing and this plays a pivotal role in creating new products and services. All these changes spell opportunity for various business entrepreneurs thereby giving room to new business ideas. It is inevitable that with the advent of new emerging businesses, laws also needs to evolve. Given the fact that Trade Mark laws directly deal with important facets of a business, the classification and description of goods and services for filing of trademark applications and protection of brands also needs to be updated from time to time to include new lines and niche areas of businesses that are shaped by demands of consumers. In this regard, it is pertinent to note that the description of goods and services that are provided during the filing of trademark applications in India needs to be in accordance with an international system of classification of goods and services commonly knowns as the Nice Classification, which India is a party to.
The Nice International Classification System for trademarks was established by the Nice Agreement in 1957 as a way to categorise goods and services pertaining to the registration of a trademark. It basically distinguishes between goods and services. Every 5 years, a new Edition of the classification was published up until 2013. Since 2013, a new version of each edition is released annually. Nice Classifications help businesses to identify the nature of the related goods or services and seek adequate intellectual property protection.
The Nice Classification facilitates the search by organizing information concerning trademarks into indexed classes thereby making it easier to conduct a thorough search which helps in identifying the trademark registrations with specificity. The classification makes the trademark easy to be acknowledged, recognized and categorises among all signatory countries. These classifications exist so that businesses registering a trademark can identify the nature of the related good or service and seek adequate intellectual property protection.
Changes in the business eco-system and advancement of technology has made certain well-known businesses a relic of the past. For example, trademark registrations which dealt with goods such as video cassettes, floppy discs, phonograph records and with respect to services by telephone or facsimile. Given such development in technology, the owners of those trademark registrations may still continue to provide goods or services that may have the same function, content or subject matter, but in different formats, such as downloadable music files, electronic publications or digital/online services. It is for this reason that the Nice Classification of goods and services are continually reviewed and updated to include within its fold new areas of businesses and services that helps brand owners to seek protection in such new areas.
The Eleventh Edition, Version 2021 of the Nice Classification will come into force on 1 January 2021.The current Eleventh Edition, Version 2020 of the Nice Classification shall continue to apply to all applications filed from 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2020. Thereafter, applications filed from 1 January 2021 will be classified in accordance with NCL (11-2021).
In light of the various changes made to the Class Headings, it is important to adopt the updated Class Headings (in parts or in whole) if the same needs to be claimed in the application.
A copy of the Class Headings and Explanatory Notes of NCL (11-2021) and updated NCL can be accessed at WIPO under following link: https://www3.wipo.int/classifications/nice/nclef/public/en/project/NC021/annex/2.
https://www3.wipo.int/classifications/nice/nclef/public/en/project/NC021/annex/4.
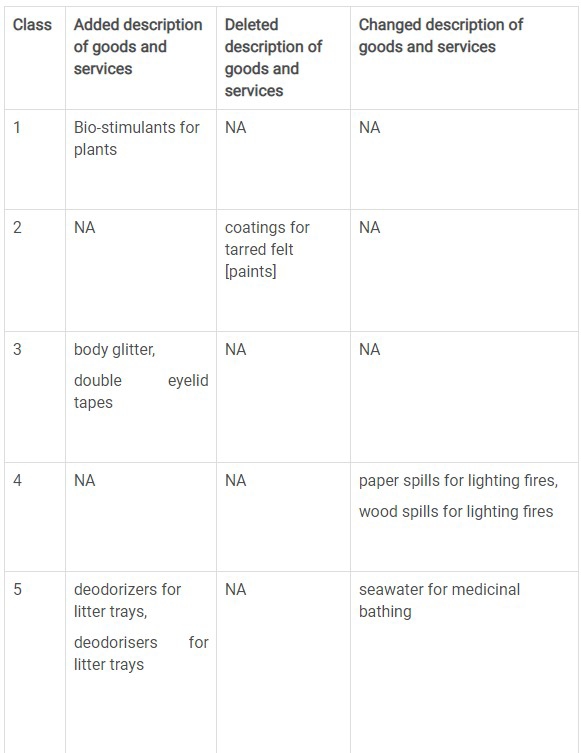
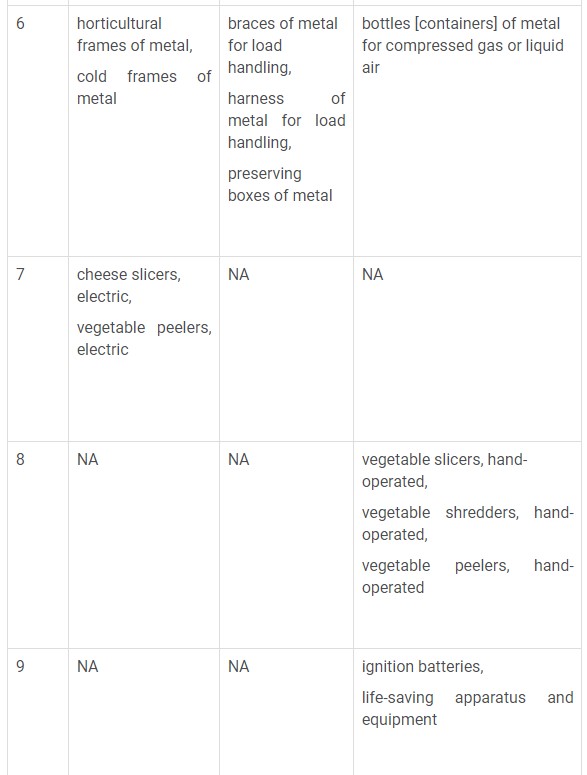
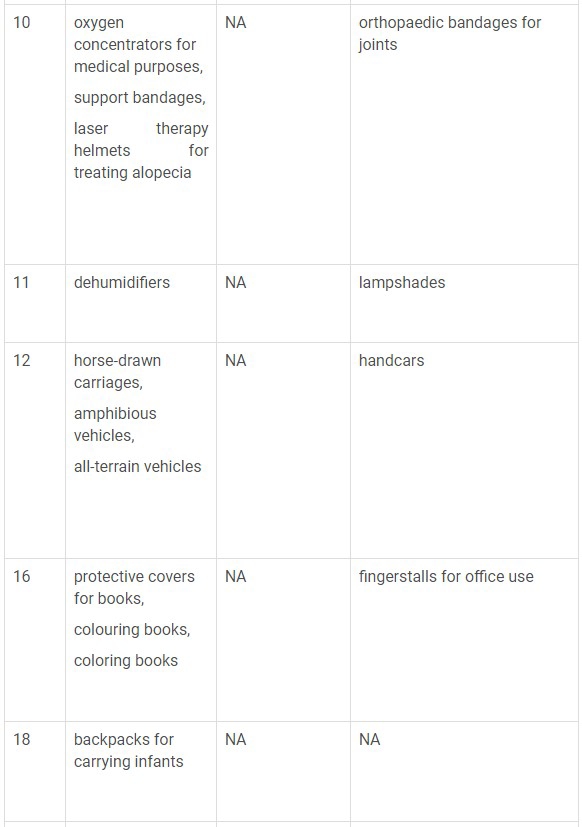
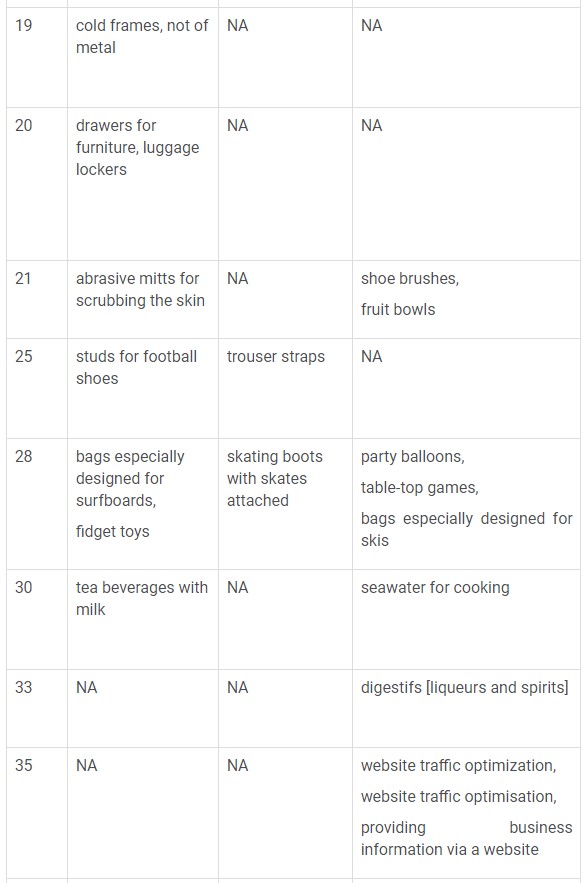
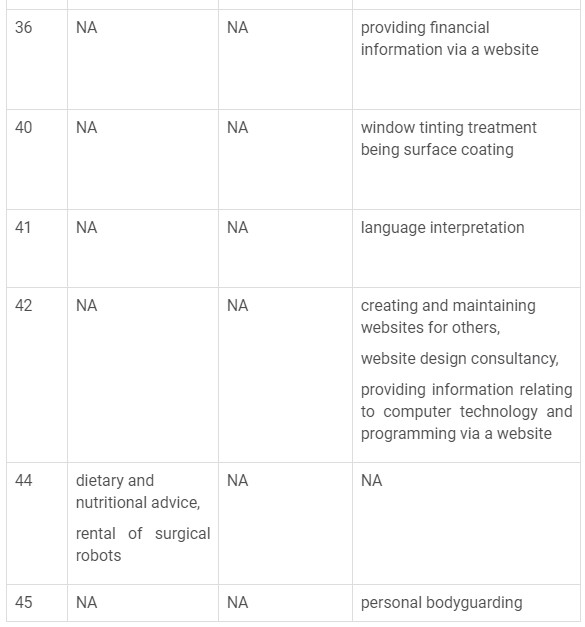
The following table captures the list of various changes in the Nice classification description that have been added, deleted and changed.